Understanding Ubuntu’s Repository System
Let's start with the essentials first. Understands the basic concept of the package manager and the repositories. This will build a foundation for you to understand how things work underneath.
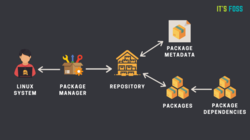
In simpler words, a package manager is a tool that allows users to install, remove, upgrade, configure and manage software packages on an operating system.
Ubuntu provides the software through repositories. The repositories contain software packages of different kinds. They also have metadata files that contain information about the packages such as the name of the package, version number, description of package and the repository name etc.
The package manager interacts with the metadata and creates a local metadata cache on your system. When you ask it to install a software, the package manager refers to this cache to get the information and then uses the internet to connect to the appropriate repository and downloads the package first before installing it on your system.